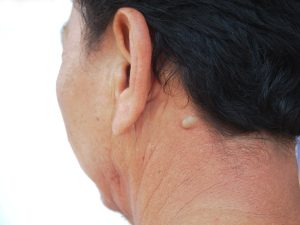
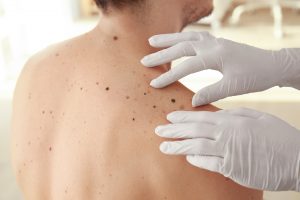
The minor surgical removal of moles, warts, cysts, lipomas and other skin lesions
What is Excision and how does it work?
Excision is a type of biopsy where a skin lesion is removed by completely cutting it out. It is typically performed using a local anesthetic to numb the area. During excision, the skin lesion is cut out using a surgical blade, as well as a small piece of normal skin from around the edges. Then, stitches are normally used to help wound healing. The sample is then sent off to be analysed in the laboratory and a full histological report will be issued.
You may choose to opt for excision of your skin lesion:
- To make a diagnosis
- To improve the cosmetic appearance
- To relieve symptoms of tenderness or inflammation
Why is Excision used by doctors?
Excision is a highly effective method for treating skin conditions, such as moles, cysts, and lipomas (fatty lumps). The procedure itself is painless and quick, usually taking about twenty to thirty minutes to complete.
What can you expect following your Excision treatment?
Afterwards, the wound may be a little sore for 7-10 days whilst it heals. We recommend that after the dressing is removed you keep the wound moist by applying Vaseline and avoid picking any scabs.